Introduction
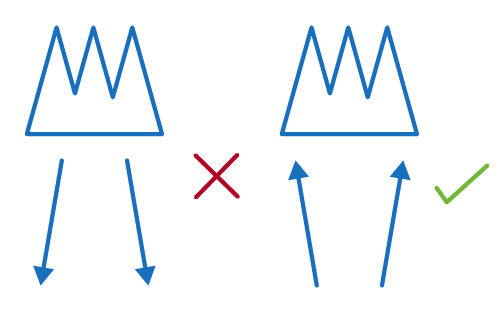
Our ecosystem is a diversified web of food chains. In this article, we will be breaking down a complicated food web to understand the different arrows and how each species is related to each other:
- Which species are both predator and prey?
- How do these species affect one another?
Let’s analyse this question on the topic of Web of Life from the 2016 Red Swastika School (RSS) P6 SA1 Examination Paper.
Read Also:
Let’s Take A Look At This Question
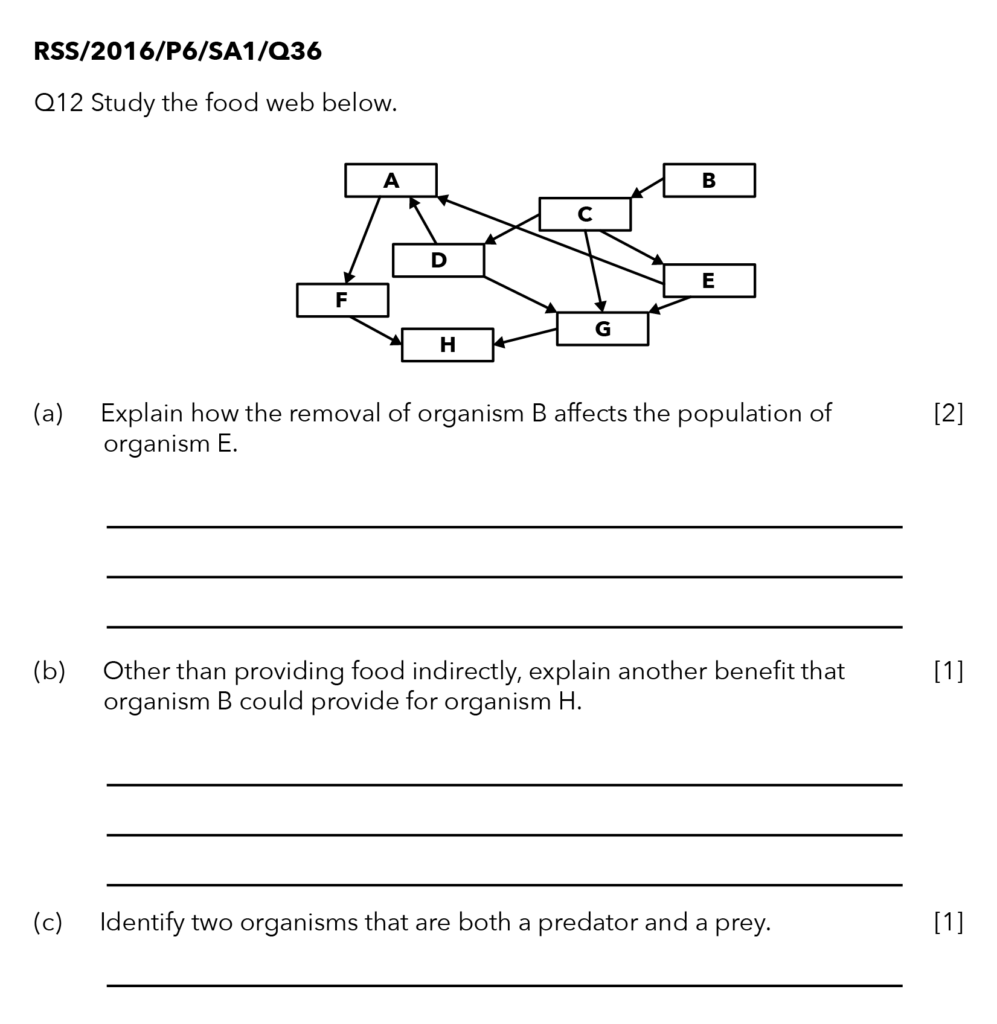
Source: Red Swastika School – 2016 P6 SA1 Examination Paper [Q36]
Thought Process
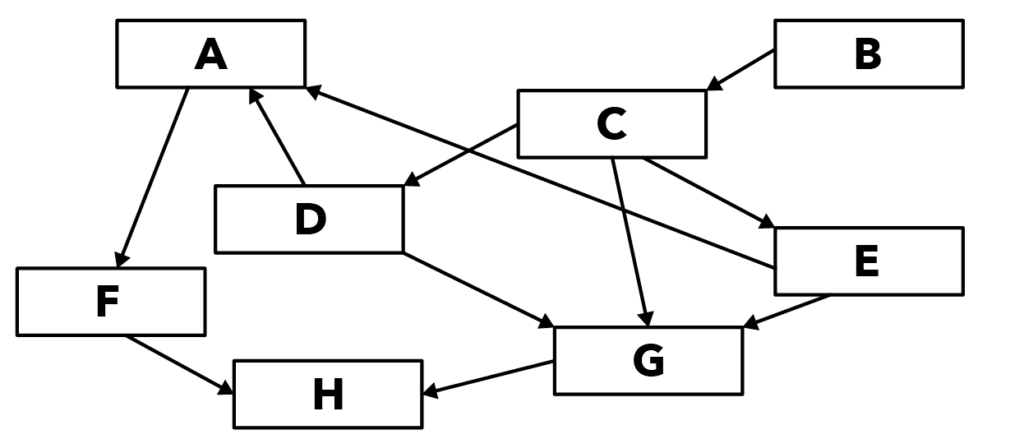
Source: Red Swastika School – 2016 P6 SA1 Examination Paper [Q36]
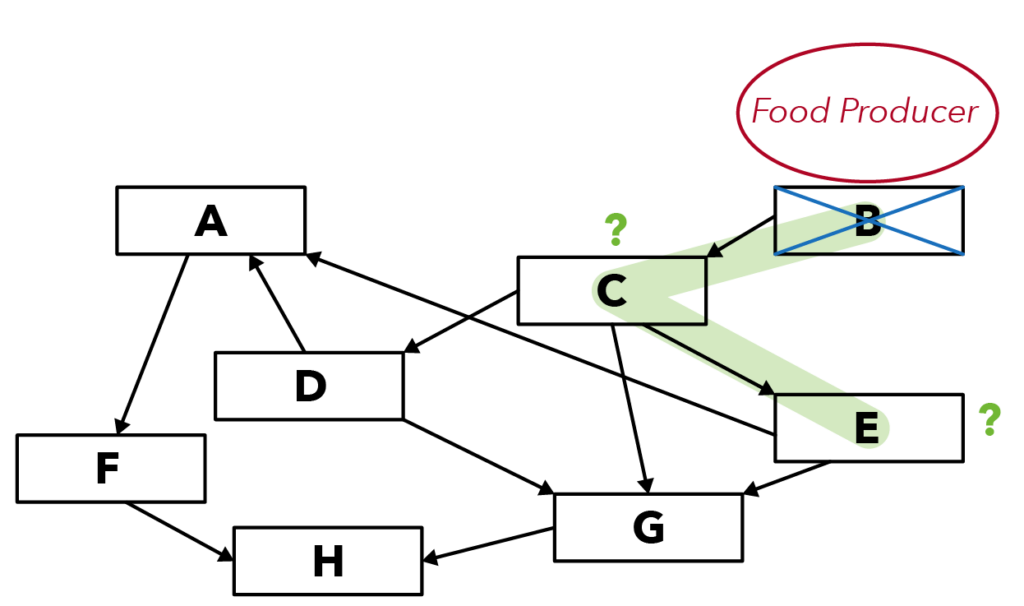
In the food web above, I want us to identify who the food producer is. To identify the food producer, we have to look at the arrows.
📍 Identifying The Food Producer 📍
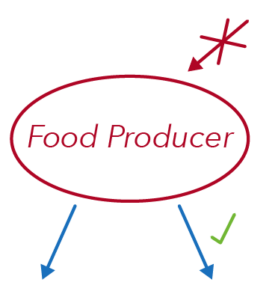
To identify the food producer, look at where the arrows are pointing at.
There should be no arrows pointing towards a food producer.
There should only be arrows pointing away from a food producer.
Can you identify the food producer in the food web above?
It is organism B!
Let’s Analyse Part (A)
Source: Red Swastika School – 2016 P6 SA1 Examination Paper [Q36]
How are organisms B and E related? They are related through C.
This means that before we find out what happens to the population of E when B is removed, we have to find out what happens to the population of organism C first.
How are organisms C and B related? C is feeding on B. But can we say that C is the predator of organism B? No!
📍 What Is A Predator? 📍
A predator feeds on another animal, not a plant.
B is a food producer, which means B is a plant. If an organism is feeding on a plant, it cannot be considered a predator.
What is C called then? It is called the “consumer” of a plant. We can say that organism C is the consumer of organism B.
What happens when the population of B is removed entirely? There will be no more food for C to feed on. The population of C would decrease.
If the population of C decreases, how will it affect the population of E?
Let’s recall: How are C and E related? E is the predator of C. What happens when the population of C decreases? The population of E would decrease as well.
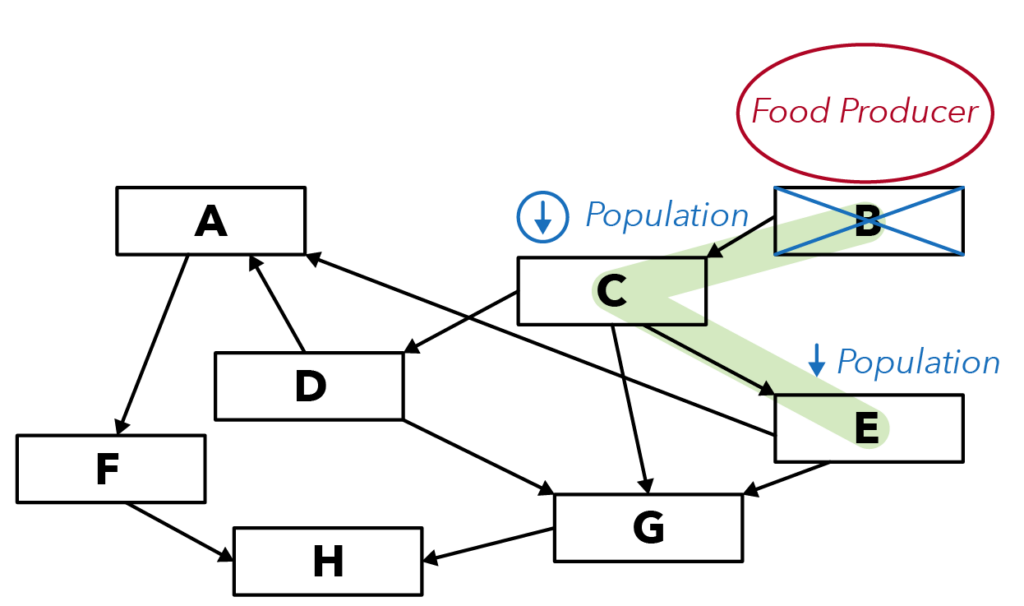
Why is that so? Because there is now less C for E to feed on, the population of E will also decrease.
We know that the population of E will decrease. How do we then structure our answer for part (a)?
📝 Use The ‘RPE’ Structure Of Writing 📝
‘R’ stands for ‘Relationship‘.
‘P‘ stands for ‘Population change’.
‘E‘ stands for ‘Effect‘.
First of all, we have to talk about how C is affected when the population of B is removed. What’s the relationship between B and C? C is the consumer of B.
What is the population change that’s happening? When organism B is removed, the population of C would decrease.
What is the effect of having organism B removed? There is no more food for C to feed on. That’s the reason why the population of C will decrease.
However, we need to use the ‘RPE’ structure of writing one more time to explain the relationship between C and E and how having less C around will affect the population of E.
Again, let’s start with “relationship”. What’s the relationship between E and C? E is the predator of C.
How about population change? When the population of C decreases, the population of E will also decrease.
There is less food for E to feed on.
Suggested Answer For Part (A)
Relationship: Organism C is the consumer of organism B.
Population change: When organism B is removed, the population of organism C will decrease,
Effect: as there is no more food for organism C to feed on.
Relationship: Organism E is the predator of organism C.
Population change: When the population of organism C decreases, the population of organism E will also decrease,
Effect: as there is less food for organism E to feed on.
Let’s Analyse Part (B)
Source: Red Swastika School – 2016 P6 SA1 Examination Paper [Q36]
What is so special about organism B? Organism B is a food producer. Food producers are also known as plants.

The question is asking, “Other than providing food indirectly, what is another benefit that a plant could provide for an animal like H?”
Think about how plants benefit animals.
🌱 What Is Photosynthesis? 🌱
Plants undergo photosynthesis, which is a process where they take in carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. They go through this process to make food.
During this process of making food, they also release oxygen.
Do animals need oxygen? Yes, they need oxygen for respiration, to release energy.
The oxygen that’s released by the plants during photosynthesis will be taken in by organism H, for respiration, to release energy. That is the benefit a plant can provide an animal.

Suggested Answer For Part (B)
Organism B is a food producer that takes in carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight for photosynthesis to make food and release oxygen. Oxygen released is then taken in by organism H for respiration to release energy.
Let’s Analyse Part (C)

Source: Red Swastika School – 2016 P6 SA1 Examination Paper [Q36]
To find out which organisms are both a prey and a predator, all we have to do is eliminate animals that are prey only, as well as the animals that are predators only. Let’s talk about the animals that are predators only.
👑 Who Are The Predators? 👑
Animals that are “predator only” means they are not a prey at all. If they’re not a prey at all, that means they do not get eaten up by any organism.
I call them the ‘king’ of the food web.
How do we identify the king of a food web? We look at the arrows. Remember, they are not prey. They don’t get eaten up by other organisms. Can you see any arrows pointing away from them? No, there should only be arrows pointing towards them.
Do you know who the king in this food web is? It is organism H. Are there any other kings? None.
Apart from eliminating the predators only, which are the kings, we have to eliminate all the prey only. That means they are not predators at all. If they’re not predators at all, that means they don’t feed on animals.
What kind of organisms don’t feed on animals? We have a special name for them. Do we call them herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
👑 Carnivores, Omnivores And Herbivores 👑
🦊 Carnivores feed on animals.
🔄 Omnivores also feed on animals, although they also feed on plants.
🌱 Herbivores don’t feed on animals at all.
Who are the herbivores in the food web then? A herbivore has to be feeding on a plant. Which organism feeds on a plant? It is C.
📍 Herbivores Are Preys Only📍
If an animal is a prey only, it is essentially a herbivore.
Is C feeding on another animal? No. Since it’s not feeding on another animal and is only feeding on plants, it is considered a herbivore.
Once again, to identify which organisms are both prey and predator, all we have to do is look for everything except the herbivores and the king. But there is another group that we have to eliminate as well.
If you’re looking for an organism that is both prey and predator, we’re talking about an animal.
Can we include a plant? No. Therefore, we have to eliminate the food producers as well.
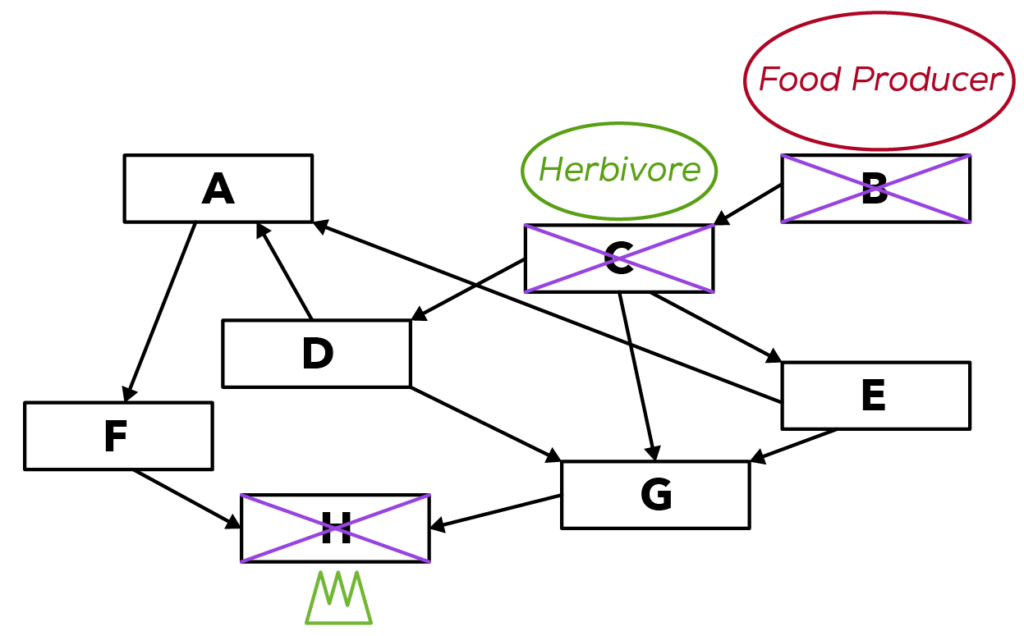
If we eliminate the food producer, the herbivores, and the king, we are left with five options. All we have to do is to just choose two of these five.
Suggested Answer For Part (C)
Choose any 2 from A, D, E, F, and G.
Conclusion
I hope this article has been an informative read for you.
Looking at a food web with many arrows pointing in different directions can be overwhelming.
But once you’ve applied the techniques I shared in this article, I hope that you’ll see these arrows as your guide in identifying an organism’s role in the food web.
The brilliant thing is that these tips can be applied to other Web of Life questions that involve food webs as well!
Check out our other articles on Web of Life and continue to keep a lookout for more articles! 🙂
If you like our methodology, we've some upcoming workshops: