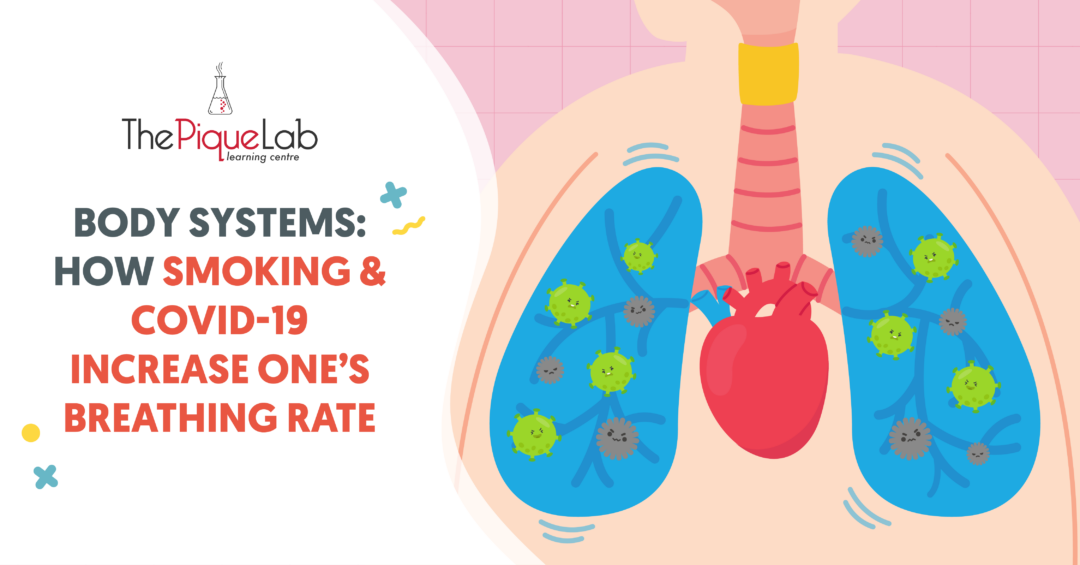
I’m pretty sure all of us have heard of the COVID-19 virus by now. It was a pandemic that shook the world in November 2019 and is ongoing even now.
Do you have any idea which body system COVID-19 affects? Let me give you a hint:
“This system is responsible for carrying out the exchange of gases.”
If your answer is “respiratory system”, you are spot on! 👍
Do you know that some COVID-19 patients with serious symptoms will experience shortness of breath and breathe faster than usual?

Now, the important question is, why do some COVID-19 patients breathe faster than usual?
To answer this question, do you recall a common scenario tested in your examinations that causes damage to the person’s respiratory system and results in the person breathing faster than usual?
If your answer is “smoking”, you are correct!
Read Also:
Today, I will be discussing a question from the 2017 Nanyang Primary School P5 SA2 Examination Paper to understand why smokers have a higher breathing rate than non-smokers.
After that, we will draw some parallels to the COVID-19 virus to explain why some COVID-19 patients breathe faster than usual.
Let’s Take A Look At This Question
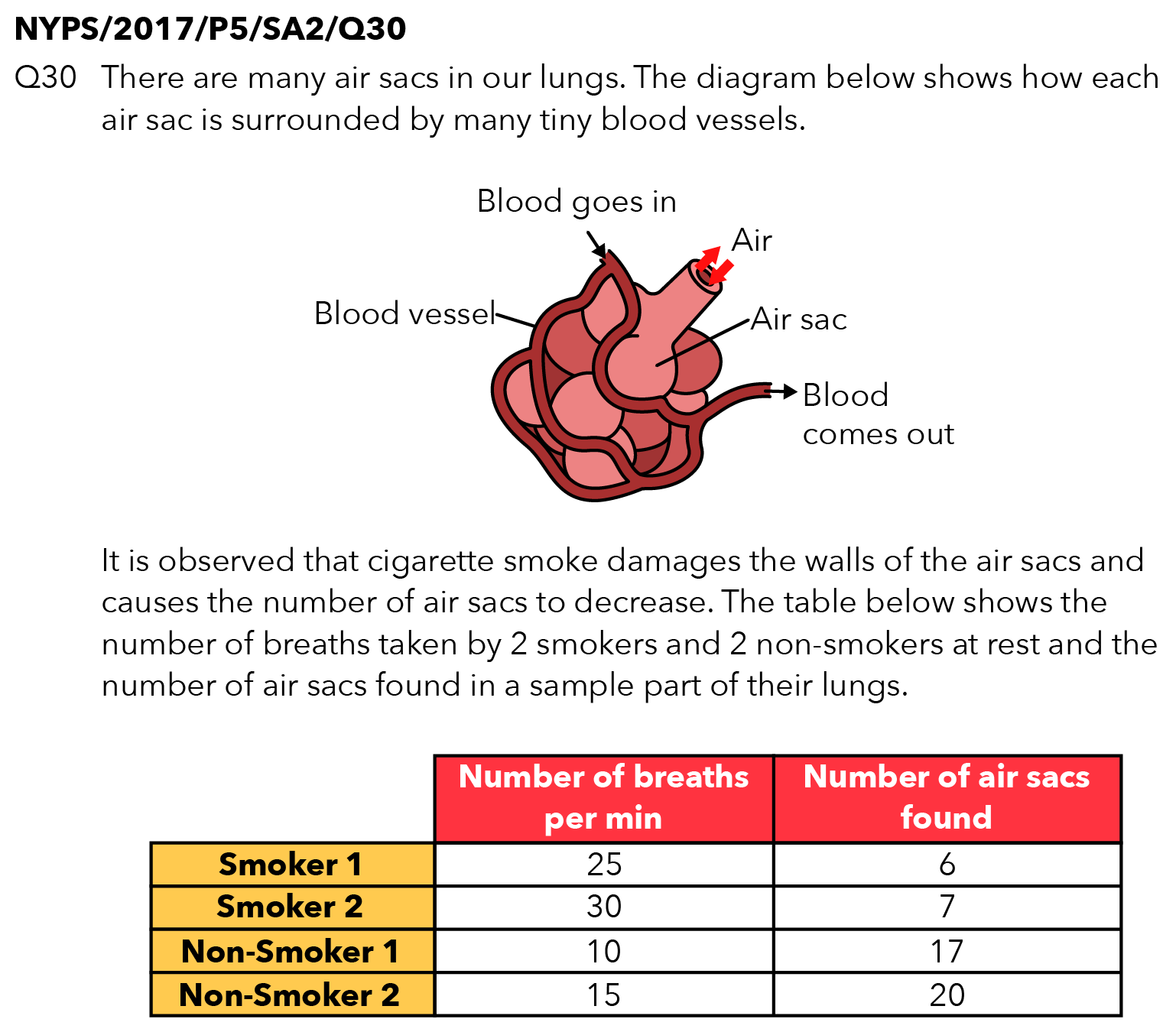
Source: Nanyang Primary School – 2017 P5 SA2 Examination Paper [Q30]
Question
Explain why the breathing rate of a smoker at rest is higher than a non-smoker at rest.
Let’s Analyse
After reading the question, some of you are thinking:
“My school has not taught me the concept of how smoking causes the breathing rate to be higher than usual. It is not fair to test me this question!”
Let me share an important tip with you below:
⭐️ Tip: For out-of-syllabus questions, sufficient data would have been provided for you to answer the question. Your job will be to read through the question carefully and highlight the relevant information that can help you to answer the question.
Since the question is comparing the difference between a smoker and a non-smoker, I am going to identify and highlight the key information in the question that differentiates smokers and non-smokers!
You can try it as well and see if it tallies with mine below!
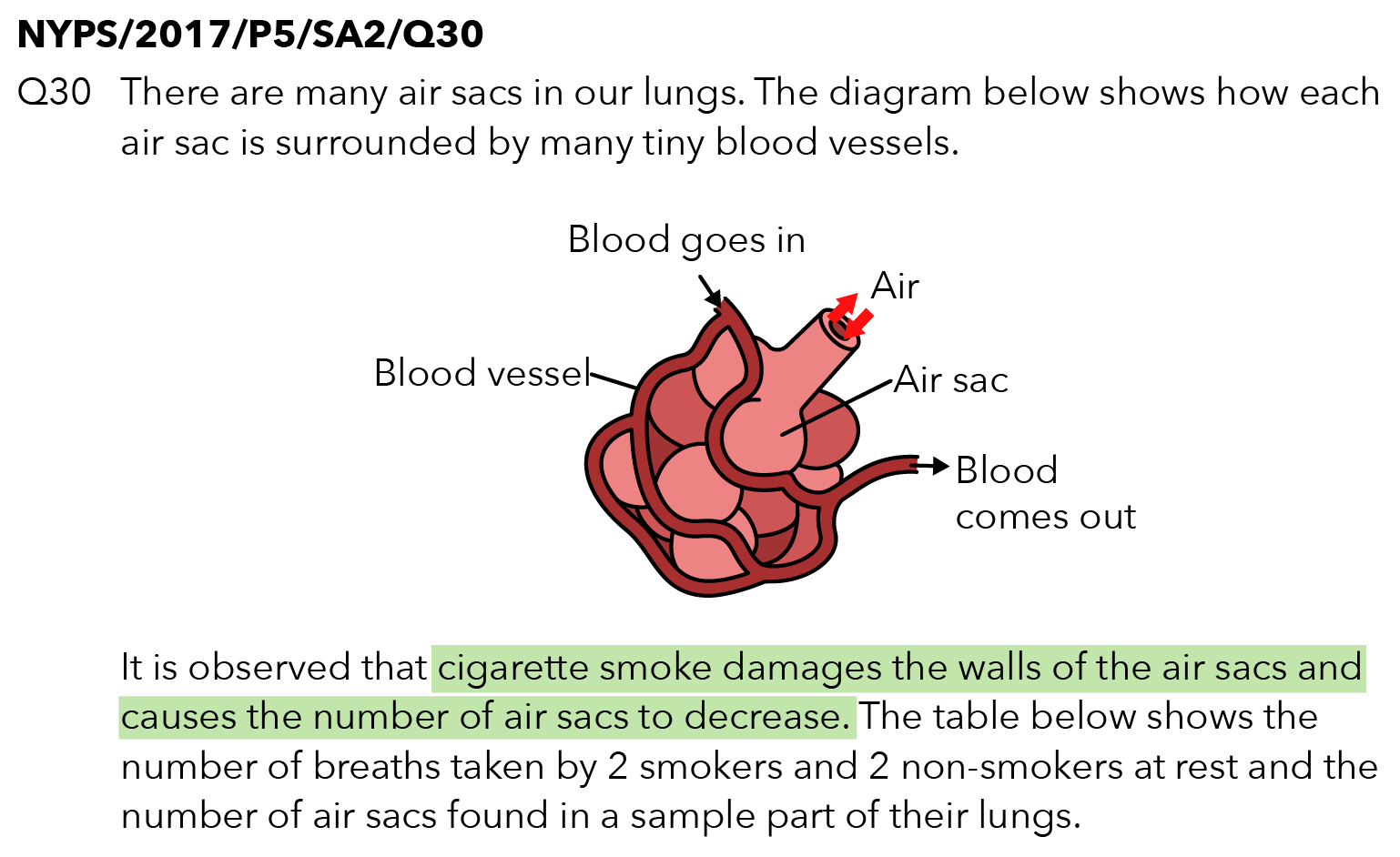
Source: Nanyang Primary School – 2017 P5 SA2 Examination Paper [Q30]
Key information: “Cigarette smoke damages the walls of the air sacs and causes the number of air sacs to decrease.”
❓ Did You Know: How does cigarette smoke damage the walls of the smoker’s air sacs?
The cigarette residue will be deposited on the inner walls of the smokers’ air sacs. Thus, these air sacs become damaged and cannot carry out exchange of gases (Refer to the diagram below).

Thought Process
Since the key information above mentioned that cigarette smoke damages the walls of the air sacs and causes the number of air sacs to decrease,
“Will there now be a larger or smaller exposed surface area of the lungs in contact with the air?”
Answer: Smaller exposed surface area.
“Due to the smaller exposed surface area, will there now be a faster or slower exchange of gases?”
Answer: Slower exchange of gases.
“Due to the slower exchange of gases, will there be more or less oxygen absorbed through the walls of the air sacs into the bloodstream after each breath?”
Answer: Less oxygen.
“Since the question specified that both the smoker and non-smoker are at rest (same activity), do they require the same amount of energy?”
Answer: Yes.
“As such, will the smoker and non-smoker both carry out the same rate of respiration to release the same amount of energy?”
Answer: Yes.
“To carry out the same rate of respiration, do the body cells of the smoker and non-smoker need to receive the same amount of oxygen to carry out respiration?”
Answer: Yes.
“Since the smoker has a slower exchange of gases in 1 breath,
but still need to receive the same (sufficient) amount of oxygen
for the same (sufficient) rate of respiration
to release the same (sufficient) amount of energy,
does the smoker have to breathe faster or slower to achieve the above?”
Answer: Faster.
Consolidating all the thought processes above, the suggested answer is as shown below.
Suggested Answer
A smoker has fewer air sacs in the lungs. This reduces the exposed surface area of the lungs in contact with the inhaled air for slower exchange of gases.
Thus, the smoker has to breathe faster to take in sufficient oxygen, which is absorbed through the air sacs into the bloodstream and is used by the body cells for respiration to release sufficient energy.
Drawing The Link Between Smoking And COVID-19
At the start of the blog post, I mentioned that some COVID-19 patients with serious symptoms breathe faster than usual.
Since smoking (as previously discussed) and COVID-19 both result in a person breathing faster than usual, the reason why both smokers and COVID-19 patients breathe faster than usual should also be similar, which is summarised from the suggested answer above:
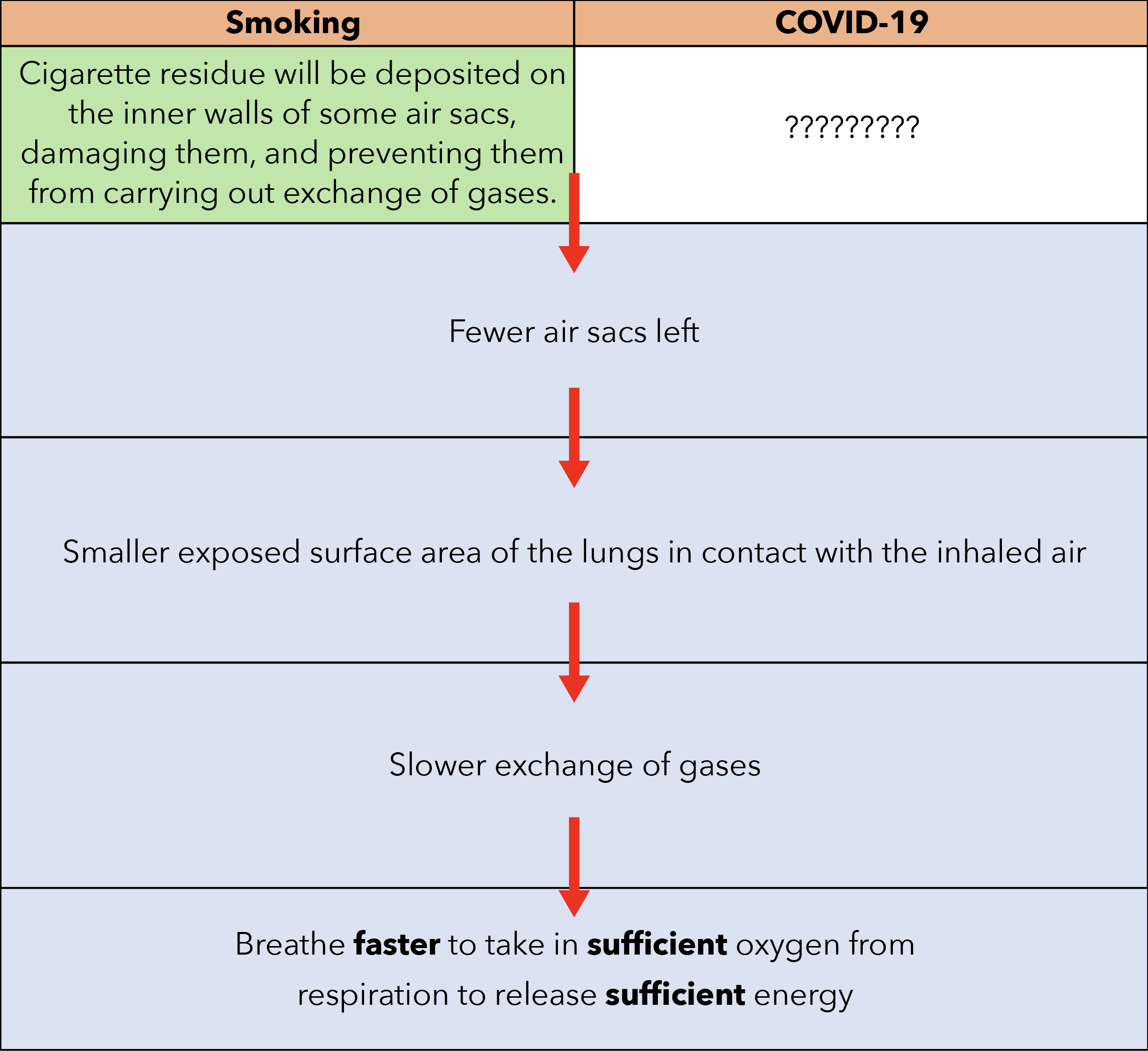
As seen from the summary table above, the only question left unanswered is:
“Instead of cigarette residues damaging the air sacs of smokers, how are the air sacs of COVID-19 patients damaged?”
When someone is infected with the COVID-19 virus, the virus enters his/her lungs in droplets, infects the cells that are lined up at the air sacs and multiply.
When this happens, the air sacs start getting inflamed and would be filled with pus and fluid.
As a result, these air sacs will be damaged and cannot carry out any exchange of gases.
This condition is what we call pneumonia, as seen in the diagram below.
Now that we have solved the mystery of how the air sacs of COVID-19 patients are damaged, let us complete the summary table above:

Let’s Take A Look At Another Question
Recently, I came across a question from the 2020 P6 SA2 CHIJ St Nicholas Girls’ School Examination Paper that tested the concept of how a person’s breathing rate will become higher when the air sacs are inflamed by a virus and filled with a lot of fluid.
Question
Organism C is a virus that causes air sacs to be filled with a lot of fluid. Explain how breathing in too much of organism C can cause a person to have a higher breathing rate.
Thought Process
Since organism C is a virus that also causes air sacs to be filled with a lot of fluid, do you recognise what organism C is from our previous discussion?
It is probably referring to the COVID-19 virus.
And what is the condition in which the air sacs are filled with a lot of fluid? It is none other than pneumonia.
Consolidating the pointers from the smoking VS COVID-19 summary table above, the suggested answer is as shown below.
Suggested Answer
Breathing in too much of organism C will reduce the exposed surface area of the air sacs in contact with the inhaled air for a slower exchange of gases.
Thus, the person has to breathe faster to take in sufficient oxygen, which is absorbed through the air sacs into the bloodstream and is used by the body cells for respiration to release sufficient energy.
Conclusion
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article and that this article has helped you gain a better understanding of:
- How smoking causes the breathing rate of a person to be faster than usual.
- How to draw parallels between smoking and COVID-19 to explain why COVID-19 patients breathe faster than usual.
Continue to keep a lookout for our new articles! 🙂
If you like our methodology, we've some upcoming workshops: